As 2024 draws to a close, the technological landscape is rapidly evolving, pushing the boundaries of what we once thought possible. Innovations in a variety of fields are not only addressing humanity’s most pressing challenges, but also paving the way for a future that could be very different from today’s.
Here’s a closer look at the top 10 technologies expected to define our future, along with the potential ethical dilemmas they pose.
1. Genomics for Transplants
In January 2024, a significant milestone was reached when David Bennett Senior became the first person to receive a genetically modified pig heart. This groundbreaking procedure in xenotransplantation holds immense promise for the over 100,000 Americans currently on organ transplant waiting lists.
- Scientists aim to genetically modify pig organs to enhance compatibility with human bodies, potentially creating an unlimited supply of transplantable organs.
- Despite its potential, this technology raises ethical concerns, particularly from animal rights activists and the risk of zoonotic diseases.
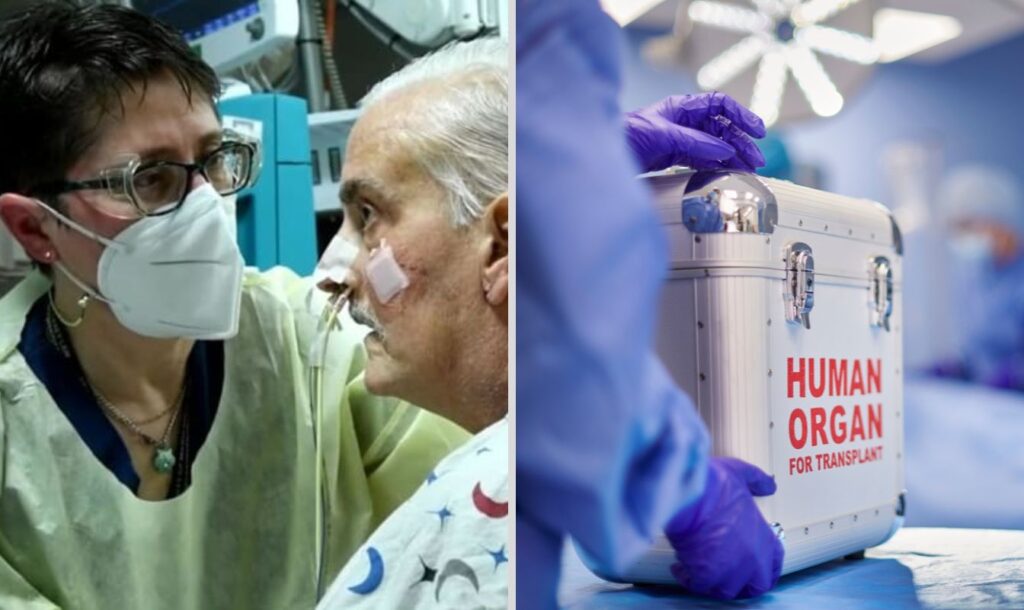

While the possibilities are vast, the ethical implications surrounding the manipulation of animal genes for human benefit must be carefully considered.
2. Alternative Livestock Feeds
As the global population continues to grow, food systems are under increasing strain. One innovative approach to address food scarcity is repurposing food waste into livestock feed.
- Globally, over 1.3 billion tons of food waste are produced annually. Utilizing this waste could significantly mitigate both food scarcity and waste management issues.
- One method involves using black soldier fly larvae to break down food waste, which can then be processed into protein-rich animal feed.
- Trials have shown that chickens fed insect-based diets can achieve growth rates comparable to those on conventional feeds.
- Another alternative is single-cell proteins derived from bacteria, yeast, or algae, which can be cultivated on industrial byproducts.

While this approach has the potential to revolutionize animal agriculture, challenges such as scaling production and consumer acceptance remain significant hurdles.
3. Carbon Capturing Microbes
In the fight against climate change, engineered microbes are emerging as unlikely heroes. Scientists are modifying certain bacteria and algae to consume CO2 more effectively.
- These microbes can convert CO2 into useful products like biofuels or biodegradable plastics. For example, the microbe cacus elongatus has been engineered to produce ethanol from CO2 with remarkable efficiency.
- At scale, these microbes could potentially sequester gigatons of CO2 annually, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
However, the stability and safety of these engineered organisms in natural environments must be ensured to avoid ecological disruptions.
4. Elastocaloric Materials
Elastocaloric materials could transform how we heat and cool our environments. These materials change temperature when stretched or compressed, potentially leading to more efficient heating and cooling systems.
- Elastocaloric systems could be 20 to 30% more efficient than traditional vapor compression systems, which are prevalent in refrigerators and air conditioners.
- Moreover, they do not rely on harmful refrigerants like hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which are potent greenhouse gases.
While promising, current elastocaloric materials, often made from nickel-titanium alloys, are expensive and can degrade over time, necessitating the exploration of more sustainable alternatives.
5. Immersive Technology for the Built World
Immersive technology is increasingly blurring the lines between the digital and physical worlds, particularly in urban planning and construction.
- Cities like Helsinki are utilizing digital twins to simulate and optimize traffic flow and energy consumption, allowing planners to test scenarios before implementing changes.
- Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing building processes by enabling workers to overlay 3D blueprints onto physical spaces, reducing errors by up to 90%.

However, as our built environments become more connected, privacy concerns arise, along with the risk of a widening digital divide where access to these technologies is not equitable.
6. Integrated Sensing and Communication
Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) technology could transform our wireless infrastructure into a comprehensive sensing system.
- ISAC utilizes radio waves not just for data transmission but also to gather environmental information, creating detailed maps of surroundings, detecting movement, and monitoring air quality.
- Applications include real-time traffic monitoring in smart cities and non-invasive patient monitoring in healthcare.

While ISAC has the potential to enhance network capacity significantly, it also raises privacy concerns, particularly regarding surveillance capabilities.
7. High Altitude Platform Stations
High Altitude Platform Stations (HAPS) function as flying cell towers, operating at altitudes of about 20 kilometers to provide internet connectivity in remote areas.
- Over 2.6 billion people in 100 countries still lack internet access, and HAPS could bridge that gap, providing educational resources and economic opportunities.
- They can be rapidly deployed in response to natural disasters, restoring communication when most needed.

However, maintaining HAPS in the air for extended periods requires advanced materials and energy systems, alongside navigating complex regulatory challenges.
8. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) are smart panels capable of dynamically altering their electromagnetic properties to enhance wireless communication.
- By redirecting signals to areas with poor coverage, RIS could increase network capacity by up to 10 times while reducing energy consumption.
- They could enable precise indoor positioning, revolutionizing industries from healthcare to manufacturing.

Despite their promise, creating surfaces that effectively manipulate signals across a wide range of frequencies remains technically challenging and potentially costly, with privacy concerns over targeted surveillance.
9. Privacy Enhancing Technologies
Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PETs) are designed to safeguard personal information in our increasingly data-driven world.
- These include advanced encryption methods and synthetic data generation, allowing for secure data analysis without compromising privacy.
- Homomorphic encryption enables computations on encrypted data, revolutionizing sectors like healthcare by allowing analysis of sensitive information without exposing it.

many of these technologies are computationally intensive, potentially slowing down systems or increasing operational costs.
10. AI for Scientific Discovery
AI is fundamentally changing how we explore and understand our world, particularly in fields like drug discovery and material science.
- The first AI-designed drug entered human clinical trials in 2023, developed in just 12 months at a fraction of the usual cost, paving the way for treatments of previously economically unfeasible diseases.
- AI is also predicting properties of new compounds, with one system identifying a new material for more efficient solar cells.
- In theoretical physics, AI has made breakthroughs, such as solving a decades-old problem in nuclear fusion by identifying optimal magnetic field configurations.

While AI’s potential is enormous, concerns about its black-box nature and the risk of perpetuating biases in training data must be addressed to ensure equitable access and prevent a scientific divide.
Conclusion
The top 10 technologies of 2024 showcase a future filled with potential and promise. However, as we innovate, it is crucial to navigate the ethical dilemmas and challenges these technologies present. Balancing the immense potential for societal benefit with thoughtful consideration of the implications will be key to shaping a better future for all.
If you have any thoughts on these technologies or their implications, feel free to share your opinions in the comments below. Together, we can explore the exciting frontier of emerging technologies and their impact on our lives
FAQs
What is xenotransplantation?
It’s the use of pig hearts for human transplants. It’s to help people who are waiting for organ donations.
How can food waste help animals?
Food waste can be turned into feed for animals, using insects or tiny organisms like bacteria.
What are carbon capturing microbes?
They are tiny organisms that eat carbon dioxide and turn it into useful things like fuel or plastics.
What are HAPS?
HAPS are flying devices that provide internet to places where it’s hard to connect.
What are Privacy Enhancing Technologies?
They are tools that protect personal data while still allowing for its safe use.
- Starlink was made available at no cost to those affected by Hurricane Helene though it isn’t completely free
- Internet of Things and Smart Cities: Tech Meets Urban
- AMD vs. Intel: Has AMD Finally Overtaken the CPU Giant?
- Harry Potter Artificial Intelligence : How Would Dumbledore Use AI in His Plans?
- Artificial Intelligence In Game Development Today
- Low Cost Drone with Camera: How to Get Pro-Quality Footage for Less

